What Is An Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram is also called an echo test. It is a test that helps visualize the heart with an ultrasound machine.
It is a valuable test that helps view the structure and function of the heart muscle, heart valves, and vessels arising from the heart.
How Is It Performed?
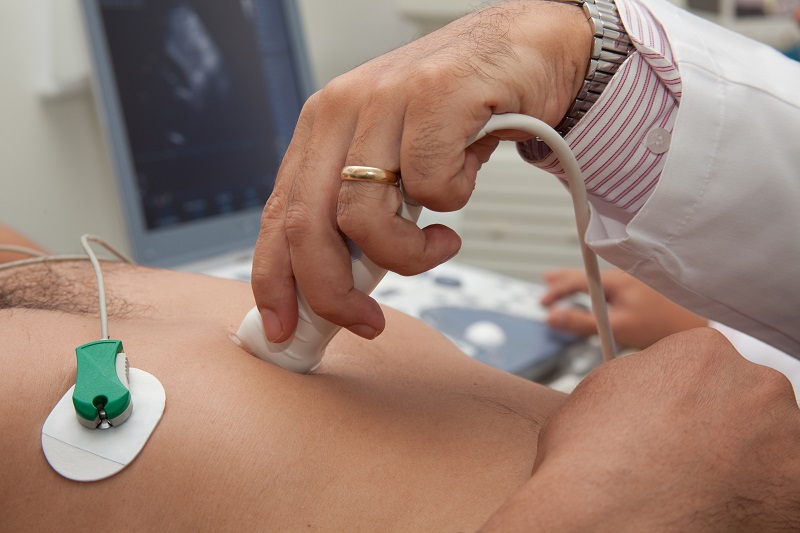
An echocardiogram (sometimes just called ‘echo’) is performed using an ultrasound machine that has capabilities for taking pictures and videos of the heart.
There are a number of buttons on the machine that aids making special measurements. On the machine is a large screen that displays all the images. Attached to the machine is a probe, which possesses small crystals, called ‘peizo-electric crystals’. These emit ultrasound waves that are converted to digital information and displayed on the screen.
The patient will be asked to attend the department for the test. There is no need to fast and no special preparation is required, unless the doctor requests so.
Prior to the test, the patient will be asked to undress to the waist and lie down on an examination couch. Women will be asked to wear a gown that opens in the front.
ECG leads are attached to the chest so that the heart can be monitored during the test.
The patient will be asked to lay on his/her left side, with the left arm tucked behind the head. The ultrasound probe is then placed on the chest and images are obtained.
The test takes between 10 – 15 minutes to perform, and is painless.
What Information Does The Test Provide?
An echocardiogram provides plenty of information in numerous heart conditions that aid diagnosis and guide treatment.
Some of the information it can provide is:
- Heart muscle structure and function – Thickness of the muscle, any scarring, any thinning of the muscle, pumping action of the muscle.
- Valve structure and function – Valve opening and closing, any infection, any leak or narrowing.
- Pericardium structure – The pericardium is a thin lining that surrounds the heart (like a protective casing). An echo can view structure and any fluid around the heart.
- Vessel structure – Assess structure of aorta, pulmonary artery and inferior vena cava.
Is The Test Painful?
Sometimes, when assessing the heart with an echocardiogram, the probe may need to be pressed firmly onto the chest. This can cause mild discomfort but does not cause any significant pain to the patient. There are no risks associated with an echocardiogram.
Limitations
The echocardiogram provides a wealth of information, and in this day and age of cardiology, the test is indispensable.
Despite this, the information obtained can be limited by body habitus and certain health conditions like lung disease, as the image quality can be poor.
In patients who have complicated heart structures, it may be difficult to make an accurate assessment. In such cases further tests may be required.
Special Tests
Echocardiography has advanced tremendously in recent years. Normal echocardiography is performed in 2-D, but newer machines can perform specialized measurements in 3-D. Furthermore, newer measures help assist in diagnosing valve problems and pumping function of the heart.